Cell Theory

- The cell theory, that all the plants and animals are composed of cells and that the cell is the basic unit of life, was presented by two biologists, schleiden (1838) and Schwann (1839).
- The cell theory was further expanded by Virchow (1855) by suggesting that all cells arise from pre-existing cells. With the discovery of the electron microscope in 1940, it was possible to observe and understand the complex structure of the cell and its various organelles.
Types of organisms
There are two types of cells:
- Unicellular
- Multicellular
- Unicellular-Those organisms which are composed of single cell are known as unicellular organisms, which perform all the function. Ex-Amoeba, Paramecium, Chlamydomonas and bacteria.
- Multicellular- Those organisms which are composed of many cells which are known as multicellular, which perform all the different functions in it to form various body parts. Ex- fungi, plants and animals.
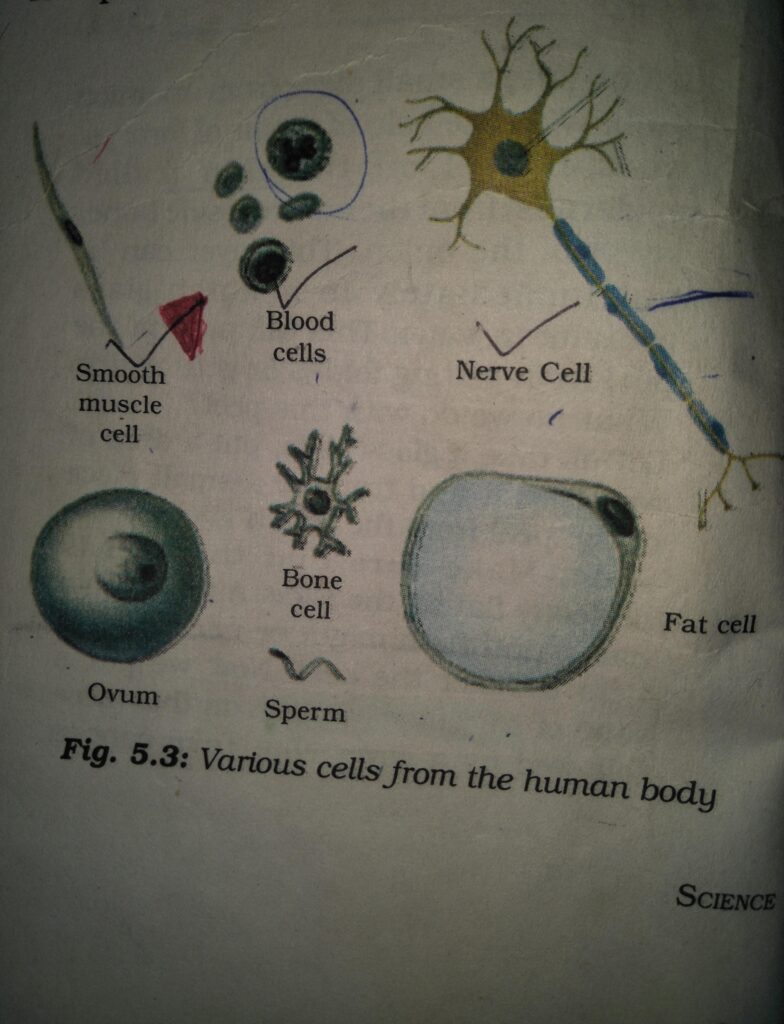
The shape and size of cells are related to the specific function they perform. Some cells like Amoeba have changing shapes could be more or less fixed and peculiar for a particular type of cell; Ex- nerve cells have a typical shape.
Each living cell has the capacity to perform certain basic functions that are characteristics of all living forms. There is a division of labour in multicellular organisms such as human beings. This means that different parts of the human body perform different functions. The human body has a heart to pump blood, a stomach to digest food and so on. Similarly, division of labour is also seen within a single cell. Each cell has got certain specific components within it known as cell organelles.
Each kind of cell organelle performs a specific function, such as making new material in the cell, clearing up the waste material from the cell and so on. A cell is able to live and perform all its functions because of these organelles. These organelles together constitute the basic unit called the cell.


