Uniform motion and Non-uniform motion

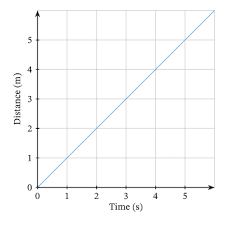
Uniform motion:- As the object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time, it is said to be in uniform motion. Example- A car running at a constant speed of say, 10 metres per second, will cover equal distances of 10 metres, every-second, so its motion will be uniform.
Non-uniform motion:- As the object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time, it is said to be in non-uniform motion. Example- If we drop a ball from the roof of a tall building, we will find that it covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
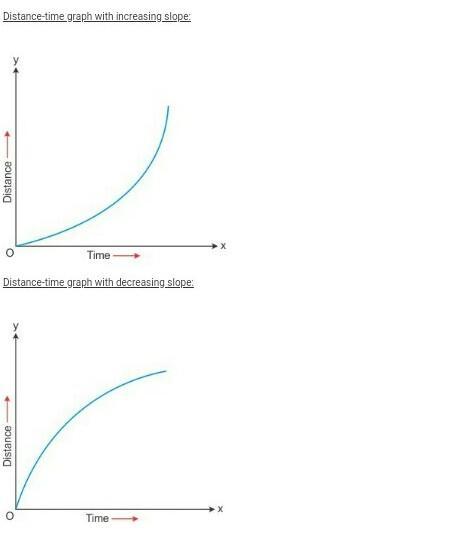
Different objects may take different amounts of time to cover a given distance. Some of them move fast and some move slowly. The rate at which objects move can be different. Also, different objects can move at the same rate.
Speed:- The measurement of distance travelled by a body per unit time is called speed. The S.I unit of speed is m/s-1 or m/s.
Speed = Distance travelled/ Time
Average speed:- The average speed of an object is obtained by dividing the total distance travelled by the total time taken.
average speed = Total distance travelled/ Total time taken
v= s/t
Example 1:- An object travels 16m in 4s and then another 16m in 2s. What is the average speed of the object?
Total distance travelled by object = 16m + 16m = 32m
Total time taken = 4s + 2s = 6s
Average speed = Total distance travelled/ total time taken
= 32m/6s = 5.33 m s-1
speed with direction:-
Velocity:- Velocity is the speed of an object moving in a definite direction. The velocity of an object can be uniform or variable. It can be changed by changing the object’s speed, direction of motion or both. When an object is moving along a straight line at a variable speed, we can express the magnitude of its rate of motion in terms of average velocity.
Average velocity is given by the arithmetic mean of initial velocity and final velocity for a given period of time.
Average velocity = initial velocity + final velocity/ 2
Vav= u + v/ 2
Speed and Velocity have the same units, that is , m s-1 or m/s.
Example 2:- The odometer of a car reads 2000 km at the start of a trip and 2400 km at the end of the trip. If the trip took 8 h, calculate the average speed of the car in km h-1and m s-1.
Distance covered by car (s) = 2400 km – 2000 km = 400 km
Time (t) = 8 h
Average speed of car (Vav) = s/t = 400km/8h
= 50 km h-1
= 50 km/ h * 1000 m/1km * 1h/ 3600s
= 13.9 ms-1
The average speed of the car is 50 km h-1 or 13.9 m s-1.


